Call Gate主要目的用來將一程式的特權等級 (Privilege Level) 轉換至另一個特權等級。舉例來說,Linux使用者利用ioctl()系統呼叫從user space (Privilege 3)進入kernel space (Privilege 0)。
Note本篇範例程式僅示範如何使用call gate,並如何利用call gate呼叫所對應的程式碼片段,所有的程式碼都運行於privilege 0。對於特權等級的轉換 (Privilege 3 -> Privilege 0),留待往後的文章再詳加探討。本篇文章僅簡單地介紹Call Gate,詳盡介紹請參考
Intel 64 and IA-32 Architectures. Software Developer's Manual. Volume 3A之5.8節。
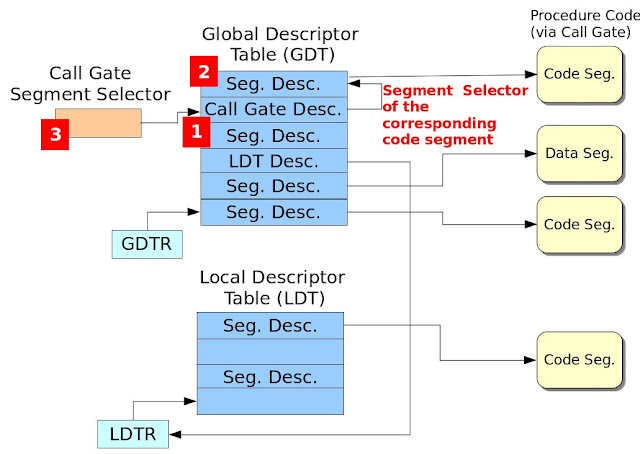
Call-Gate Descriptor之介紹參考Figure 1,其欄位如下所述:
- Offset: 代表所指定的程式區段 (Code Segment)進入點 (Entry Point),通常都設為0。
- Segment Selector: 此區段選擇器指定所要存取的程式區段 (Code Segment)。如此說明或許有點模糊,請參考Figure 2,此圖紅色數字方塊展示出設定Call Gate的必要程序,因此設定Call Gate需要三道步驟:A. 設定Call Gate Descriptor相關欄位,其欄位設定值如Table 1所示。B. 設定對應之程式區段。C. 設定Call-Gate之區段選擇器。
- Param. Count: 指定呼叫程序 (Calling Procedure)欲傳遞幾個參數給被呼叫的程序 (Called Procedure)。
- DPL (Descriptor Privilege Level): 此區段描述子之特權等級,其DPL與RPL特權等級之檢查請參考Intel 64 and IA-32 Architectures. Software Developer's Manual. Volume 3A之Figure 5-11。
- P: 此Call-Gate描述子是否有有效 (有效: P=1, 無效: P=0)。
Figure 1. Call-Gate Descriptor
Figure 2. Steps for Configuring Call Gate
Table 1. Field Value Configuration for Call-Gate Descriptor
Boot Loader程式碼請參考
此篇文章的"Boot Loader 程式碼"。
作業系統程式碼Figure 3為作業系統程式碼,此作業系統程式碼運行於32位元保護模式,程式說明如下:
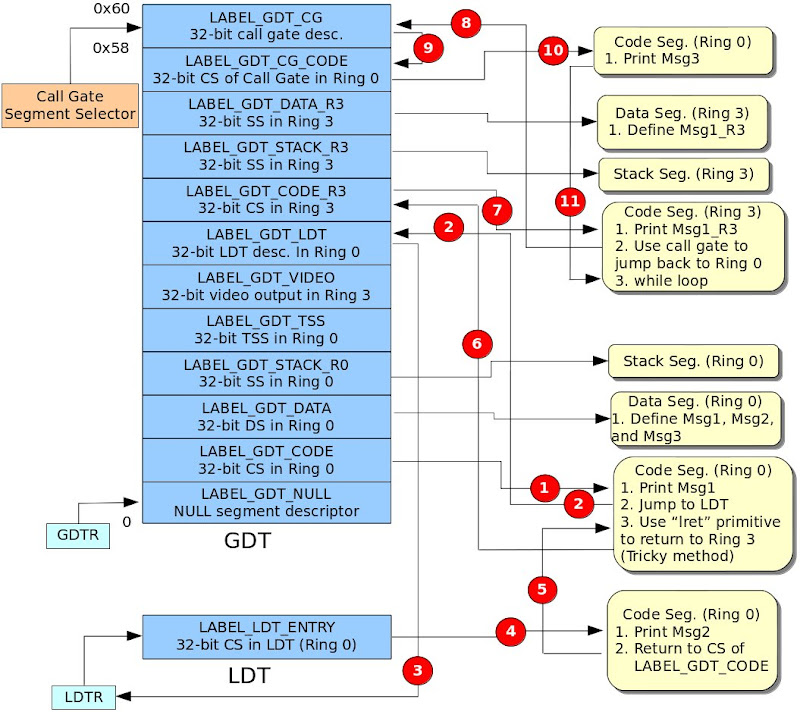
- 定義七個Segment Descriptor (LABEL_GDT_NULL、LABEL_GDT_CODE、LABEL_GDT_DATA、LABEL_GDT_VIDEO、LABEL_GDT_LDT、LABEL_GDT_CG_CODE與LABEL_GDT_CG)。其中VIDEO的基底位址為0xB8000,詳情請參考Printing to Screen。接著定義GDT的長度、定義Code、Data、VIDEO與LDT的segment selector、定義輸出的字串、定義GDTPtr與定義LDT表。
- LABEL_GDT_CG為Call Gate Descriptor,其儲存在GDT。此設定步驟為Figure 2的1號紅色方塊。
- LABEL_GDT_CG_CODE為Call Gate Descriptor欄位Segment Selector所指定的地方,也就是Call Gate所對應的區段程式碼。此設定步驟為Figure 2的2號紅色方塊。
/* os.S
*
*/
#include "pm.h"
.code16
.text
jmp os_main
# Segment descritors for GDT
LABEL_GDT_NULL: SEG_DESC 0, 0, 0
LABEL_GDT_CODE: SEG_DESC 0, (PECode32Len - 1), (DESC_ATTR_TYPE_CD_ER | DESC_ATTR_D)
LABEL_GDT_DATA: SEG_DESC 0, (DataLen - 1), (DESC_ATTR_TYPE_CD_RW)
LABEL_GDT_VIDEO: SEG_DESC 0xB8000, 0xFFFF, (DESC_ATTR_TYPE_CD_RW)
LABEL_GDT_LDT: SEG_DESC 0, (LDTLen - 1), (DESC_ATTR_TYPE_LDT)
LABEL_GDT_CG_CODE: SEG_DESC 0, (CG_CODE32_LEN - 1), (DESC_ATTR_TYPE_CD_ER | DESC_ATTR_D)
LABEL_GDT_CG: CALL_GATE SegSelectorCGCODE, 0, 0, (GATE_CG_ATTR)
# The length of GDT
.set GdtLen, (. - LABEL_GDT_NULL)
# Segment selectors
.set SegSelectorCode32, (LABEL_GDT_CODE - LABEL_GDT_NULL)
.set SegSelectorData, (LABEL_GDT_DATA - LABEL_GDT_NULL)
.set SegSelectorVideo, (LABEL_GDT_VIDEO - LABEL_GDT_NULL)
.set SegSelectorLDT, (LABEL_GDT_LDT - LABEL_GDT_NULL)
.set SegSelectorCGCODE, (LABEL_GDT_CG_CODE - LABEL_GDT_NULL)
.set SegSelectorCG, (LABEL_GDT_CG - LABEL_GDT_NULL)
# data segment
LABEL_DATA:
Msg1: .ascii "Welcome to Protect mode in GDT.\0"
Msg2: .ascii "Welcome to Protect mode in LDT.\0"
Msg3: .ascii "Welcome to Protect mode through Call Gate.\0"
.set Msg1Offset, (Msg1 - LABEL_DATA)
.set Msg2Offset, (Msg2 - LABEL_DATA)
.set Msg3Offset, (Msg3 - LABEL_DATA)
.set DataLen, (. - LABEL_DATA)
# GDTR pointer
LABEL_GDTR:
.2byte (GdtLen - 1) # Limit field
.4byte 0 # base field
# LDT information
LABEL_LDT:
LABEL_LDT_ENTRY: SEG_DESC 0, (LDT_CODE32_LEN - 1), (DESC_ATTR_TYPE_CD_E | DESC_ATTR_D)
# length of LDT
.set LDTLen, (. - LABEL_LDT)
# LDT selector
.set SegSelectorLDTCode32, (LABEL_LDT_ENTRY - LABEL_LDT + SA_TIL)
# real-mode OS code
os_main:
mov %cs, %ax
mov %ax, %ds
mov %ax, %ss
mov %ax, %es
/* Set gdt for code segment */
InitSegDescriptor LABEL_PE_CODE32, LABEL_GDT_CODE
InitSegDescriptor LABEL_DATA, LABEL_GDT_DATA
InitSegDescriptor LABEL_LDT, LABEL_GDT_LDT
InitSegDescriptor LABEL_PE_LDT_CODE32, LABEL_LDT_ENTRY
InitSegDescriptor LABEL_PE_CG_CODE32, LABEL_GDT_CG_CODE
/* Set GDTR */
xor %ax, %ax
mov %cs, %ax
shl $4, %eax
addl $LABEL_GDT_NULL, %eax
movl %eax, (LABEL_GDTR + 2)
/* Enable A20 line */
xor %ax, %ax
in $0x92, %al
or $2, %al
out %al, $0x92
cli
/* Load the GDT base address and limit from memory into the GDTR register */
lgdt LABEL_GDTR
/* Enable protect mode */
movl %cr0, %eax
orl $1, %eax
movl %eax, %cr0
/* Jump to protected-mode OS code */
ljmp $SegSelectorCode32, $0
LABEL_PE_CG_CODE32:
.code32
mov $(SegSelectorData), %ax
mov %ax, %ds
mov $(SegSelectorVideo), %ax
mov %ax, %gs
xorl %esi, %esi
xorl %edi, %edi
movl $Msg3Offset, %esi
movl $((80 * 11 + 0) * 2), %edi
movb $0xC, %ah
cg_dump_str:
lodsb
andb %al, %al
jz cg_fin
mov %ax, %gs:(%edi)
addl $2, %edi
jmp cg_dump_str
cg_fin:
lret
.set CG_CODE32_LEN, (. - LABEL_PE_CG_CODE32)
LABEL_PE_LDT_CODE32:
.code32
# invoke a procedure call throught a call-gate.
lcall $(SegSelectorCG), $0
mov $(SegSelectorData), %ax
mov %ax, %ds
mov $(SegSelectorVideo), %ax
mov %ax, %gs
xorl %esi, %esi
xorl %edi, %edi
movl $Msg2Offset, %esi
movl $((80 * 13 + 0) * 2), %edi
movb $0xC, %ah
ldt_dump_str:
lodsb
andb %al, %al
jz ldt_fin
mov %ax, %gs:(%edi)
addl $2, %edi
jmp ldt_dump_str
ldt_fin:
jmp .
.set LDT_CODE32_LEN, (. - LABEL_PE_LDT_CODE32)
# protected-mode OS code in GDT
LABEL_PE_CODE32:
.code32
/* Load data segment selector */
mov $(SegSelectorData), %ax
mov %ax, %ds
/* Load Video segment selector */
mov $(SegSelectorVideo), %ax
mov %ax, %gs
/* Output the data */
xorl %esi, %esi
xorl %edi, %edi
movl $Msg1Offset, %esi
movl $((80 * 10 + 0) * 2), %edi
movb $0xC, %ah
dump_str:
lodsb
andb %al, %al
jz fin
mov %ax, %gs:(%edi)
addl $2, %edi
jmp dump_str
fin:
/* Load LDT selector */
mov $(SegSelectorLDT), %ax
/* Load LDT selector in GDT to LDT register */
lldt %ax
/* Jump to code segment in LDT */
ljmp $(SegSelectorLDTCode32), $0
.set PECode32Len, (. - LABEL_PE_CODE32)
.ascii "Welcome to OS context!"
.byte 0
.org 0x400, 0x41 # fill characters with 'A'. Sector 2
Figure 3. Operating System Codepm.h標頭檔/* pm.h
*
* Adrian Huang (adrianhuang0701@gmail.com)
*/
.macro SEG_DESC Base, Limit, Attr
.2byte (\Limit & 0xFFFF)
.2byte (\Base & 0xFFFF)
.byte ((\Base >> 16) & 0xFF)
.2byte ((\Attr & 0xF0FF) | ((\Limit >> 8) & 0x0F00))
.byte ((\Base >> 24) & 0xFF)
.endm
.macro InitSegDescriptor OFFSET GDT_SEG_ADDR
xor %ax, %ax
mov %cs, %ax
shl $4, %eax
addl $(\OFFSET), %eax
movw %ax, (\GDT_SEG_ADDR + 2)
shr $16, %eax
movb %al, (\GDT_SEG_ADDR + 4)
movb %ah, (\GDT_SEG_ADDR + 7)
.endm
.macro CALL_GATE SegSelector, Offset, ParamCount, Attr
.2byte (\Offset & 0xFFFF)
.2byte (\SegSelector)
.byte (\ParamCount)
.byte (\Attr)
.2byte ((\Offset >> 16) & 0xFFFF)
.endm
.set DESC_ATTR_TYPE_LDT, 0x82 /* LDT Segment */
.set DESC_ATTR_TYPE_CG, 0x8C /* Call-Gate Segment */
.set DESC_ATTR_TYPE_CD_ER, 0x9A /* Code segment with Execute/Read */
.set DESC_ATTR_TYPE_CD_E, 0x98 /* Code segment with Execute Only */
.set DESC_ATTR_TYPE_CD_RW, 0x92 /* Data segment with R/W */
.set DESC_ATTR_D, 0x4000 /* 32-bit segment */
/* Selector Attribute */
.set SA_TIL, 0x4
.set SA_RPL0, 0x0
.set SA_RPL1, 0x1
.set SA_RPL2, 0x2
.set SA_RPL3, 0x3
/* The attribute of call gate */
.set GATE_CG_ATTR, 0x8C
編譯程式碼下圖為編譯的Makefile。
LD=ld
CC=gcc
all: boot_loader.bin
boot_loader.bin: boot_loader.o os.o
${LD} -Ttext=0x7C00 -s $< -o $@ --oformat binary ${LD} -Ttext=0x0 -s os.o -o os.bin --oformat binary cat os.bin >> $@
boot_loader.o:
${CC} -c boot_loader.S
os.o:
${CC} -c os.S
clean:
rm -f boot_loader.o os.o os.bin boot_loader.bin
其編譯訊息如下所示:
adrian@adrian-desktop:~/working/build_os/my_ex/blog/pe-call-gate-same-priv$ make clean all
rm -f boot_loader.o os.o os.bin boot_loader.bin
gcc -c boot_loader.S
gcc -c os.S
ld -Ttext=0x7C00 -s boot_loader.o -o boot_loader.bin --oformat binary
ld -Ttext=0x0 -s os.o -o os.bin --oformat binary
ld: warning: cannot find entry symbol _start; defaulting to 0000000000000000
cat os.bin >> boot_loader.bin
adrian@adrian-desktop:~/working/build_os/my_ex/blog/pe-call-gate-same-priv$
QEMU測試結果
【Reference】
[1]
Solrex - 使用開源軟體-自己動手寫作業系統[2]
Intel 64 and IA-32 Architectures. Software Developer's Manual. Volume 3A[3]
30天打造OS!作業系統自作入門[4]
Jserv's Blog[5]
X86 開機流程小記[6]
Linux assemblers: A comparison of GAS and NASM[7] linux-source-2.6.31